7 Describe the Nomenclature Used for Chiral Amino Acids
If the hydroxyl group attached to the highest chiral carbon is on the right-hand side it is referred to as D-series and if on the left-hand side it is called L-series. Chiral amino acids present in nature are mainly classified into essential amino.
19 13 Amino Acids Chemistry Libretexts
Nomenclature Part 1 Section A.
. So the compound can exist as a pair of nonsuperimposable mirror images. All of the methods for synthesizing amino acids we have described produce racemic mixtures. Essential amino acids must be acquired through diet.
Within this class are the. CO OH R N H 2 and H where R is a variant carbon chain. The system that is used to designate the configurations of chiral carbons of naturally occurring compounds is called the D and L convention or system.
1 Aliphatic straight and branchedchain amino acids such as glycine alanine valine leucine and isoleucine the 2 Aromatic amino acids phenylalanine tyrosine and tryptophan and the 3 unique nonpolar amino acids prolineand methionine. It does not denote the absolute stereo configuration of a molecule. The central carbon has four different groups attached.
All naturally occurring proteins from all living organisms consist of L amino acids. A rule of thumb for determining the D L isomeric form of an amino acid is the CORN rule. IUPAC Amino acids codes IUPAC Amino acids codes used in bioinformatics.
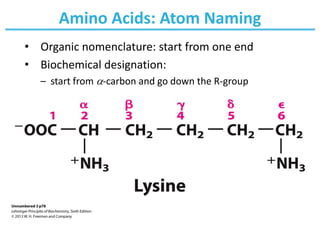
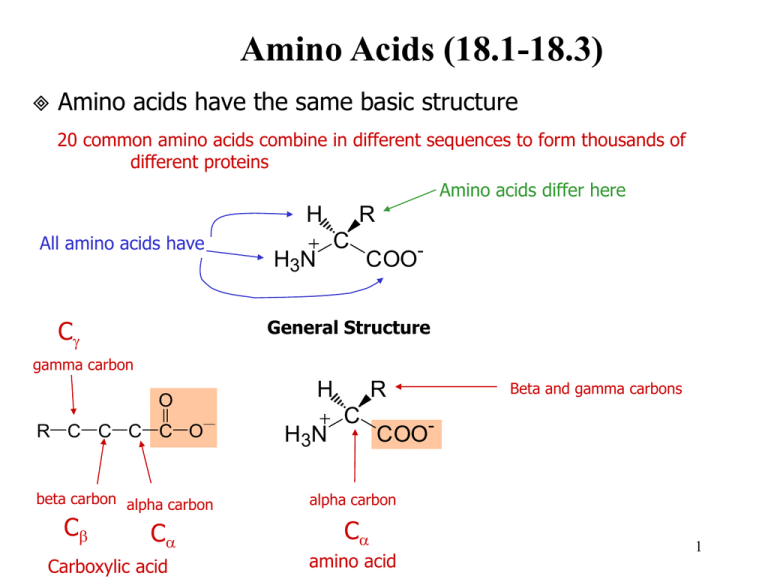
They can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups as alpha- α- beta- β- gamma- γ- or delta- δ- amino acids. Thus we can have D- and L-isomers of amino acids. The RS system of naming chiral centers A relative ranking of the priority of various functional groups is given as.
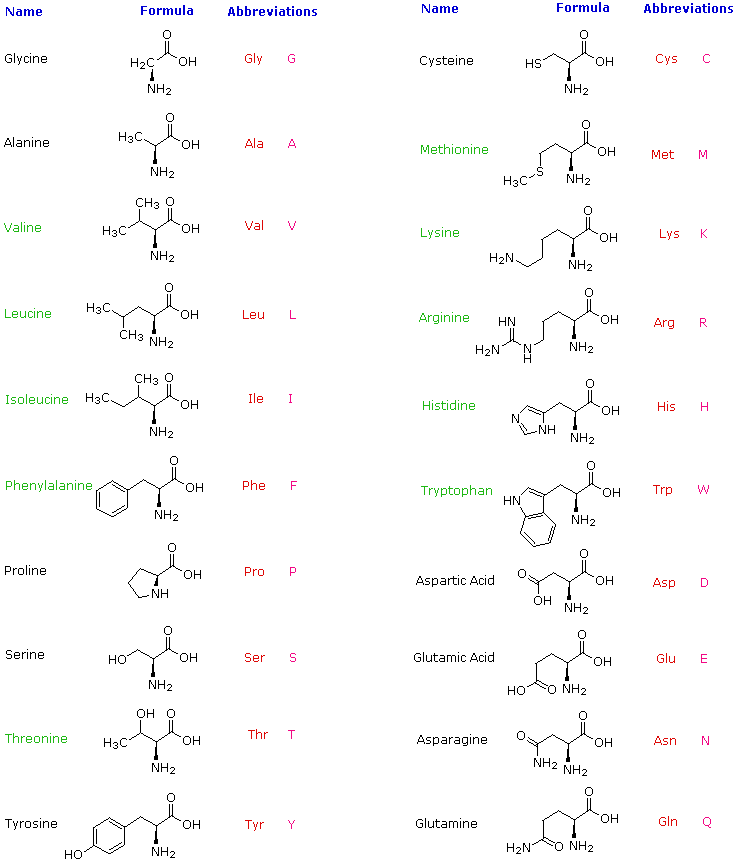
Some other common amino acids are listed in the. Other categories relate to polarity ionization and side chain group type aliphatic acyclic aromatic containing hydroxyl or. Identify the functional group with the lowest priority.
NOMENCLATURE OF CHIRAL COMPOUNDS The terminology used to describe different stereochemical properties is resumed as following 8 - 10. Common food sources for these amino acids include eggs soy protein and whitefish. Definition An optical isomer can be named by the spatial configuration of its atoms.
Nine of the nineteen L -amino acids commonly found in proteins are dextrorotatory at a wavelength of 589 nm and D - fructose is also referred to as levulose because it is levorotatory. 1 1 R CO2H HNH2 Amino Acid R sidechain 20 common amino acids 19 are 1ツー-amines 1 proline is a 2ツー-amine 19 amino acids are 窶彡hiral窶1 glycine is achiral RH The conuration of the 窶從atural窶amino acids is L 2 CH O CH2OH H O H D-glyc eraldehyde CH CH O L-g lycra dh C O2H CH3 H2N H CH R N L-alanine CO2H H2N H H O H CH3 COH 2N 3C H H2. Note that the D- and L-designations are specific terms used for the way a molecule rotates plain polarized light.
We recall however that racemic mixtures can be resolved by chiral chromatography Section 88. Asparagine was the 1st amino acid discovered and isolated from protein of Asparagus in 1806 and the last of the 20 amino acids discovered was threonine. Chirality also sometimes called stereoisomerism or enantiomerism or dissymmetry is a property of an object which is non-superimposable with its mirror image.
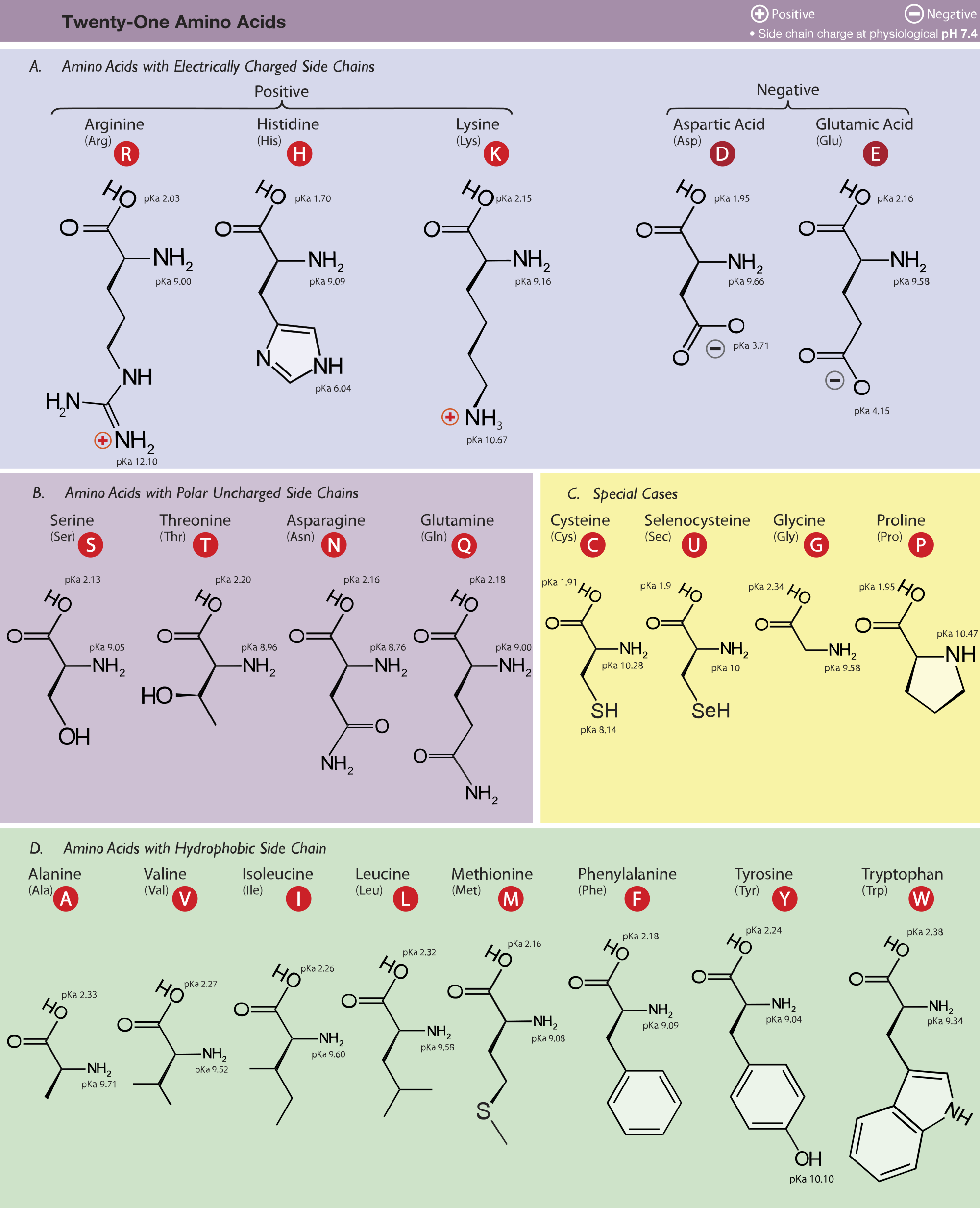
10 And thePolar Hydrophilic Amino Acids. Amino Acids are assigned DL configurations on the basis of the spatial position of the four substituents attached to the asymmetric C atom relative to those of glyceraldehyde -H -H right -NH2 -OH left -COOH -CHO top -R -CH2OH bottom How does stereochemistry play. Nonpolarhydrophobic amino acids 2.
Similar to hydroxy acids chiral amino acids can be classified into α- β- γ- ω-amino acids according to different positions of the amino group attached to the carbon chain. A rule of thumb for determining the DL isomeric form of an amino acid is. These are classed as acidic or basic respectively amino acids NH2C CO2H CH2 H CO2H Aspartic acid Naming amino acids You do not need to know any common names for the 20 essential amino acids.
1 SH OH NH 2 COOH CHO CH 2 OH CH 3 H A chiral center has four different functional groups. Basic amino acids which have a net positive charge at neutral pH. The resulting thiohydantoin derivatives of individual dl-amino acids were completely separated with isocratic elutions using acidic mobile phase involving 01 TFA.
We can also use organometallic reagents as chiral catalysts Section 178 to produce chiral amino acids as we will see in the next section. SH OH NH 2 COOH CHO CH 2 OH CH 3 H A chiral center has four different functional groups. Acidic amino acids which have a net negative charge at pH 70 4.
The α-carbon atom is thus a chiral center. For all the common amino acids except glycine α -carbon is bonded to four different groups. The RS system of naming chiral centers A relative ranking of the priority of various functional groups is given as.
Biochemists most often use the L and D nomenclature to denote stereochemistry. They are histidine isoleucine leucine lysine methionine phenylalanine threonine tryptophan and valine. NAMES OF COMMON a-AMINO ACIDS The trivial names of the a-amino acids that are commonly found in proteins and are represented in the genetic code together with their symbols systematic names 14 and formulas are given in Table 1.
Amino acids that can not be produced naturally are called essential amino acids. This nomenclature system has also become obsolete. The separations of the thiohydantoins yielded from acidic basic neutral hydroxyl and aromatic amino acids were good enough for the identification of dl-amino acid.
Amino acids are typically classified by the polarity of their side chains. Amino Acid IUPAC code Three letter code Systematic Name Formula. The standard amino acids have been assigned three letter abbreviations and one letter symbols eg for Glycine Gly is the abbreviation and G is the symbol.
But D-L-system of naming is still employed to designate the configuration of amino acids and sugars. All amino acids except glycine are chiral because they all contain at least one chiral centre. Neutral uncharged but polar amino acids 3.
A carboxyl group an amino group an R group and a hydrogen atom in case of glycine the R group is another hydrogen atom. We should however be able to name given amino acids using IUPAC organic naming 2-aminobutanedioic acid NH2CH2CO2H 2-aminoethanoic acid NH2C CO2H.

Amino Acid Stereochemistry R And S Vs D And L Configuration Youtube
No comments for "7 Describe the Nomenclature Used for Chiral Amino Acids"
Post a Comment